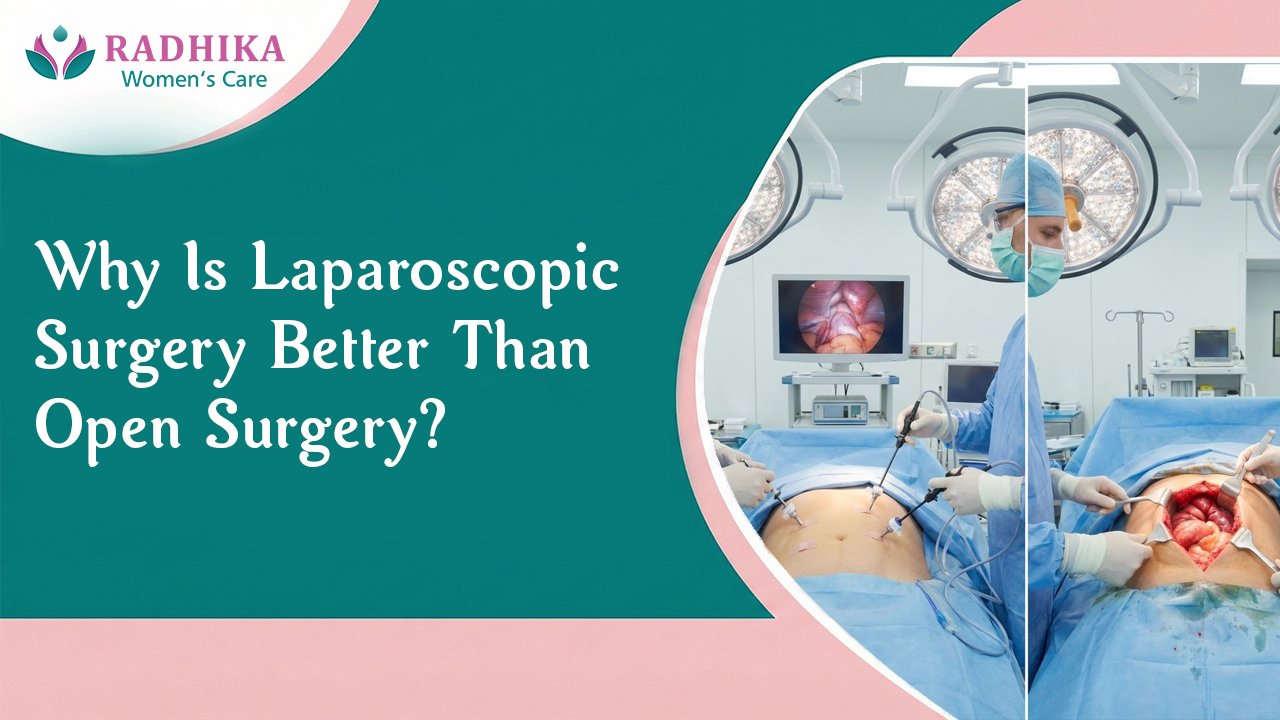
A woman scheduled for surgery for fibroids, an ovarian cyst, or endometriosis may hear two choices and feel stuck: laparoscopy or a bigger incision. Laparoscopic surgery is often better for many common gynecologic procedures because recovery is usually faster, pain is often lower, scars are smaller, and hospital stays can be shorter. But open surgery may be safer or necessary in more complex cases. This guide explains the difference, what recovery can feel like, and what to ask your surgeon.
Open surgery vs Laparoscopic surgery: what each one means
Laparoscopic surgery meaning: A surgeon makes a few small cuts, then uses a tiny camera and slim tools to do the procedure. Many people also hear this called a laparoscopy operation or “keyhole” surgery. The camera shows the inside of the abdomen on a screen, which helps the surgeon work carefully.
Open surgery meaning: The surgeon makes one larger incision so they can see and reach the area directly. Both types usually use general anesthesia. Both follow strict safety and sterile steps. The goal is the same: treat the problem in the safest way.
What happens during a laparoscopy operation (step by step)
- The patient gets general anesthesia and is fully asleep.
- The surgeon makes a few small incisions.
- A camera and small instruments go in through the openings.
- The surgeon removes, repairs, or treats the tissue (depending on the condition).
- The tools come out and the incisions are closed with stitches or surgical glue.
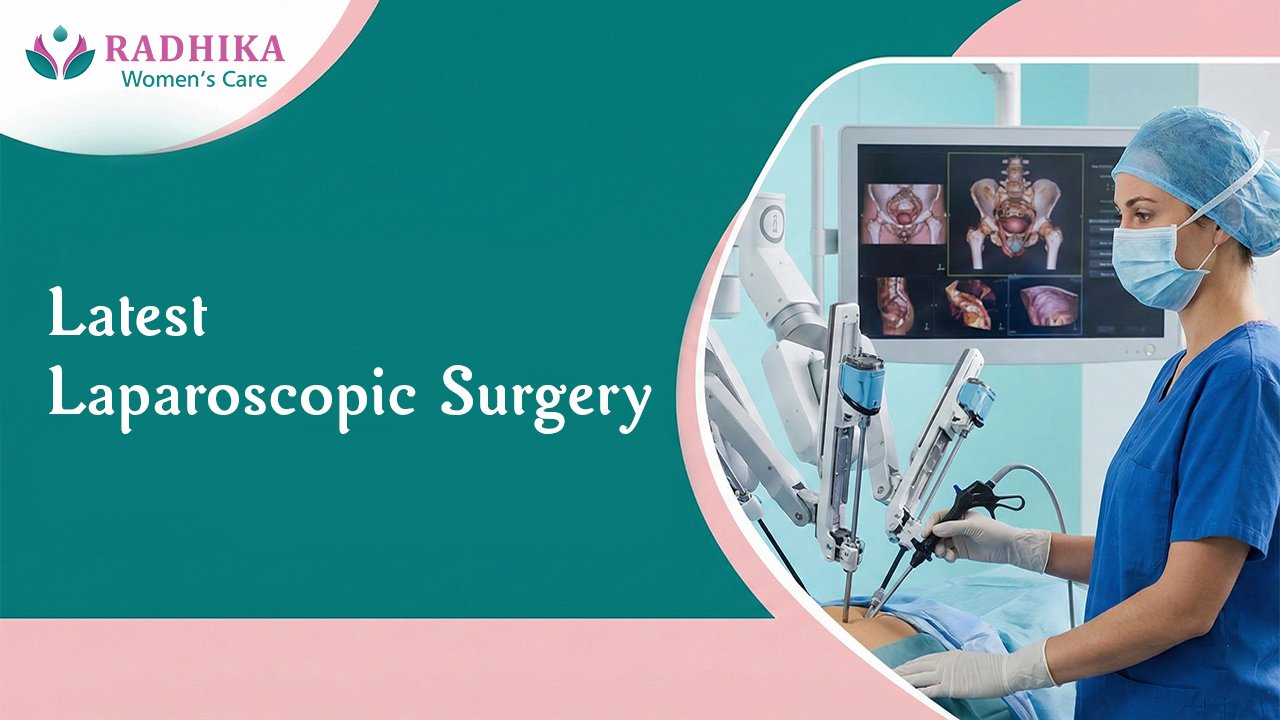
Some laparoscopic surgeries use robotic help. The goal is still the same: small incisions and careful work.
What happens during open surgery (and why the incision is bigger)
In laparoscopic vs open decisions, open surgery gives the surgeon more space and direct access. This can matter if there is a very large fibroid, a large cyst, heavy scar tissue (adhesions), or an emergency. The bigger incision helps the surgeon work safely and quickly when needed.
Open vs laparoscopic: the main differences patients feel
For many benign (non-cancer) problems, laparoscopy vs open surgery often comes down to recovery versus access. Many recent reviews (2024 to 2025) report that overall success can be similar when surgeons are experienced. Laparoscopy often has less blood loss and fewer wound problems on average.
Recovery is one of the biggest differences patients notice:
- After laparoscopy, many people can do light activity in about 1 to 2 weeks, with fuller recovery around 3 to 4 weeks for many benign cases.
- After open surgery, light activity often takes about 4 to 6 weeks, and full recovery may take 6 to 8 weeks or longer.
A 2024 matched study in large uteri reported lower median blood loss with minimally invasive approaches (about 27.5 to 50 mL) compared with open surgery (about 200 mL). Exact numbers can vary by diagnosis, size, and surgeon technique.
Read More: What Is Laparoscopic Surgery? Procedure, Uses & Benefits
Quick comparison table: laparoscopic vs open surgery
| Feature | Laparoscopic surgery | Open surgery |
| Incision size | Several small cuts | One larger cut |
| Pain | Often less | Often more |
| Hospital stay | Same day to 1 to 2 days (many cases) | Often longer |
| Return to work | Often sooner | Often later |
| Scarring | Usually smaller | Usually larger |
| Infection risk | Often lower for wounds | Often higher for wounds |
| Cost | May be higher due to tools | May be lower in some settings |
| When open is preferred | Complex cases, emergencies, heavy scarring | When visibility or speed is needed |
Pros and cons list: open surgery vs laparoscopic surgery
Laparoscopic pros
- Smaller scars
- Often less pain
- Often shorter hospital stay
- Often faster return to daily life
Laparoscopic cons
- Can take longer in the operating room
- Not always possible for very large masses
- Rare risks when entering the abdomen (your surgeon can explain)
Open surgery pros
- Wide access and room to work
- Helpful for large masses, dense adhesions, or emergencies
- May be preferred for some complex cancer surgeries
Open surgery cons
- Longer recovery
- Larger scar
- Higher risk of wound issues compared with laparoscopy in many cases
When open surgery may be better than laparoscopic surgeries
Open surgery vs laparoscopic surgery is not one size fits all. Open surgery may be recommended when:
- The uterus or fibroids are very large
- An ovarian cyst is very large, or there is concern for cancer
- There are severe adhesions from past surgeries or infections
- The plan involves certain complex cancer operations
- There is an emergency, such as heavy bleeding
Sometimes a surgeon starts with laparoscopic surgery and then switches to open surgery during the operation. This is called conversion. It is usually done for safety, not because something “went wrong.”
Questions to ask the surgeon before choosing laparoscopic vs open
- Which approach fits this diagnosis (fibroids, cysts, endometriosis) best, and why?
- What recovery timeline should I expect for my specific case?
- What is the pain control plan (meds, nerve blocks, activity limits)?
- How experienced are you with both laparoscopic and open surgery for this problem?
- What is my chance of conversion from laparoscopy to open?
- How could this surgery affect fertility or future pregnancy?
- What symptoms after surgery mean I should call right away?
- When can I return to work, driving, exercise, and sex?
FAQ
Is laparoscopic surgery better than open surgery?
Often yes for many benign gynecologic procedures because recovery is usually faster and scars are smaller. But open surgery can be safer in complex cases.
Is laparoscopic surgery safer?
It can be as safe as open surgery when done by an experienced surgeon and when the case is a good fit for laparoscopy.
Is laparoscopy more painful?
Most patients report less pain than open surgery, but everyone’s experience is different.
How long is recovery after laparoscopy vs open?
Many people return to light activity in 1 to 2 weeks after laparoscopy and need 4 to 6 weeks after open surgery. Full recovery is often about 3 to 4 weeks vs 6 to 8+ weeks.
Is laparoscopic surgery always possible?
No. Size, scarring, cancer concerns, and emergencies can change the safest plan.
Is laparoscopic surgery more expensive overall?
It depends. The operating room cost can be higher, but shorter hospital stays and faster return to work may lower total costs. Insurance coverage varies.
Which is better for endometriosis, fibroids, and ovarian cysts?
Many cases can be treated laparoscopically, especially when the goal is faster recovery. Open surgery may be better for very large disease, severe adhesions, or cancer concern.
Conclusion
For many gynecologic procedures, laparoscopic surgery vs open surgery often favors laparoscopy because recovery is usually faster and scars are smaller. Still, open surgery can be the safest choice for large, complex, or urgent cases. Encourage patients to bring these questions to a pre-op visit or book a consultation with a board-certified OB-GYN. After surgery, severe pain, heavy bleeding, fever, chest pain, or shortness of breath needs urgent medical care.